Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Radiographs, poisoning (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/7/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 9/8/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Radiographs studies can be valuable in poisoning diagnosis, management, and prognosis. Radiographic imaging should be utilized for the following toxins:
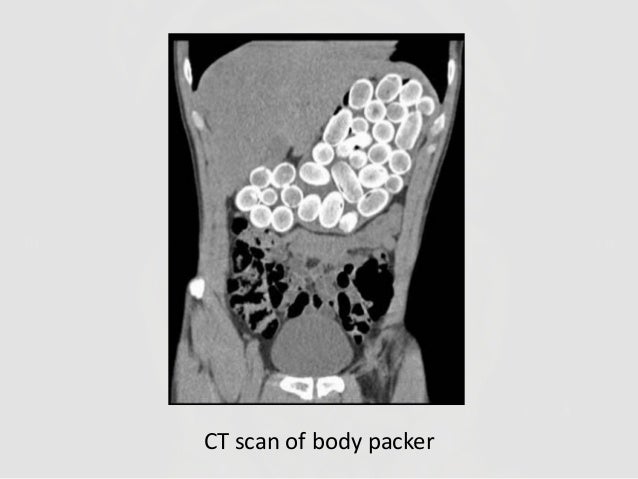
Container toxins - Body packers
Sustained Released preparations
Plain adominal radiography: a powerful tool to prognosticate outcome in patients with zinc phosphide. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Shahnazi M, et al. Clin Radiolol. 2014. Oct;69 (10);1062-5.
Systemic Plumbism following remote ballistic injury, Reinboldt M, Franics K, Emerg Radio. 2014 Aug:21 (4): 423-6.
Lead arthropathy: radiographic, CT, and MRI findings, Fernandes JL, Rocha AA, et al. Skeletal Radiol. 2007 Jul;36(7):647-57.
Intentional Intravenous Mercury injection. Yudelowitz G. S Afr Med J. 2017 Jan 30;107(2):112-114.
The role of radiology in diagnosis and management of drug mules: an update with new challenges and new diagnostic tools. Schulz B. Grossbach A, et al. Clin Radiol. 2014 Dec;69(12)
