Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Hemodialysis, lithium (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/16/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 11/17/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Lithium salts have been used therapeutically for over a 150 years to sucessfully treat manic depressive symptoms, schizoaffective disorder, and cluster headaches. Lithium has a narrow therapeutic range (0.6-1.5 meq/L) and is 100% eliminated by the kidneys. Multisystem toxicity occurs however CNS toxicity is significant and consist of confusion, lethargy, ataxia, neuromuscular excitability (tremor, fasciculations, myoclonic jerks, hyperreflexia). Since there is a poor relationship between serum concentration and toxicity in the brain, serum blood levels may not reflect extent of toxicity . The goal of enhanced elimination is to prevent irreversible lithium-effectuated neurotoxcity which causes persistant cerebellar dysfunction with prolonged exposure of the CNS to high lithium levels.
Decision for hemodialysis is determined by clinical judgement after considering factors such as lithium concentration, clinical status of patient, pattern of lithium toxicity (acute vs. chronic), concurrent interacting drugs, comorbid illnesses, and kidney function. Strongly consider hemodialysis for the following:
Extracorpeal treatment for Lithoum Poisoning: Systematic Review and Recommendations from the EXTRIP Workgroup. Decker BS, et al. Clin Am Soc Nephrology 2015 Jan
The Syndrome of irreversible lithium-effectuated neurotoxicity. Adityjee, et al. Clin Neuropharmacol. 2005 Jan-Feb;28(1):38-49.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Hemodialysis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/2/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
The cornerstone treatment of poisoning is removal of the toxin from the patient. This can be accomplished before absorption into the body by decontamination methods (dermal or gastrointestinal) or after absorption by blocking metabolism of parent compound, displacing drugs from receptors, binding toxins with neutralizing agents (chelators, Fab fragments), or enhancing elimination by dialysis. Toxins that are ideal candidates for dialysis include substances that are low molecular weight, have low volume of distribution (stay in the blood stream), or low protein binding. Toxins most commonly treated with dialysis are:
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Cannabinoid, cyclic vomiting, Capsaicin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/12/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Cannabinoid hyperemesis is a syndrome (CHS) characterized by severe intractable nausea, cyclical vomiting, and abdominal pain associated with chronic marijuana abuse. It is often a underrecognized cause of cyclic vomiting syndrome. Despite well established anti-emetic properties of marijuana, paradoxical effects on the GI tract exist through cannabinoid receptors which exert their neuromodulatory properties in the central nervous system and the enteric plexus. Multiple theories of mechanism of CHS are in the literature. Diagnosis is based on the following clinical criteria:
Acute care goals are to treat dehydration and terminate nausea and vomiting. Administration of intravenous fluids, dopamine antagonists, topical capsaicin cream, and avoidance of narcotic medications are recommened treatment measures. Benzodiazepines followed by haloperidol and topical capsaicin are reported to be most effective. Capsaicin activates the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptors (TRPV1) which impairs substance P signalling in the area postrema and nucleus tract solitarius similar to noxious stimuli, such as heat.
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome: Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment-a Systematic Review. Sorensen CJ, DeSanto K, et al. J Med Toxicol. 2017 Mar;13(1):71-87.
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis and Compulsive Bathing: A Case Series and Paradoxical Pathophysiological Explanation. Patterson D, Smith E, et al. Am Board Fam Med. 2010 Nov-Dec; 23(6): 790-793.
Pharmacologic treatment of cannabinoid hyperemesis Syndrome: A systematic review. Pharmacotherapy. Dezieck L, Hafez Z. 2017 Jun:37(6):725-734.
Resolution of cannabis hyperemesis syndrome with topical capsaicin in the emergency department: a case series. Dezieck L, Hafez Z, et al. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017 Sep;55(8):908-913.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Capsaicin, hunan hand, chili peppers (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/6/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Hunan hand syndrome is a painful contact dermatitis that frequently presents in cooks and chili pepper workers after preparing or handling chili peppers. Contact with other body parts gives rise to the terms: "Hunan nose" ''Hunan eye",and "Chili Willie". Capsaicin, found in the fruit of plants from the genus Capsicum such as red chili peppers, jalapeños, and habaneros, is a hydrophobic, colorless, odorless compound that binds with pain receptors causing the sensation of intense heat or burning. The "heat" or pungency of a peppers is measured in Scoville heat units (SHU), the number of times a chili extract must be diluted with water to lose heat. Habanero peppers generate 30,000 SHU. Even at low concentrations capsaicin is a skin irritant. It is the primary ingredient in pepper spray used in law enforcement and in personal defense sprays.
Treatment consists of decontamination with water irrigation for opthalmic exposure and milk or antacids for dermal or gastrointestinal exposure. Burning can be recurrent and of of long duration depending on tissue penetration. Topical anesthetic especially for the eye and cool compresses for the skin can relieve pain. Parodoxically capsaicin is used as a topical analgesic medication for local pain relief from muscle pain, itching, and painful neuropathies (diabetic, postherpetic). Capsaicin initially causes neuronal excitation followed by a long-lasting refractory period due to depletion of substance P, during which neurons are no longer responsive to a large range of stimuli and thus are desensitized.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Hyperkalemia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/22/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 10/5/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Hyperkalemia is a potentially life threatening problem which can lead to cardiac dysrhythmias and death. Drug interactions inducing hyperkalemia are extremely common such as the combination of ACE inhibitors and spironolactone or ACE inhibitors and trimehoprim sulfamethoxazole. Hyperkalemia can also occur with a single agent and is a relatively common complication of therapy with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole. The following drugs can cause hyperkalemia:
Drug induced hyperkalemia. Salem B. Badreddine A, et al. Drug Safety 2014 Sept;37(9) 677-92.
Beta-blockers, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and the risk of hyperkalemia requiring hospitalization in the elderly: a nested case-control study. Weir MA, Juurlink DN, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:1544-1551.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Radiographs, poisoning (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/7/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 9/8/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Radiographs studies can be valuable in poisoning diagnosis, management, and prognosis. Radiographic imaging should be utilized for the following toxins:
Container toxins - Body packers
Sustained Released preparations
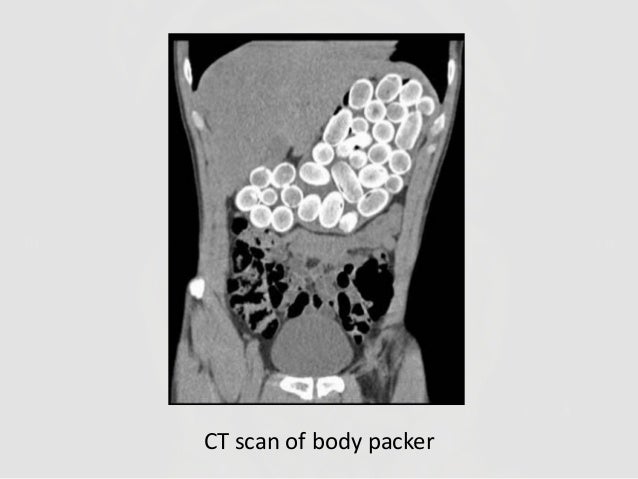
Plain adominal radiography: a powerful tool to prognosticate outcome in patients with zinc phosphide. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Shahnazi M, et al. Clin Radiolol. 2014. Oct;69 (10);1062-5.
Systemic Plumbism following remote ballistic injury, Reinboldt M, Franics K, Emerg Radio. 2014 Aug:21 (4): 423-6.
Lead arthropathy: radiographic, CT, and MRI findings, Fernandes JL, Rocha AA, et al. Skeletal Radiol. 2007 Jul;36(7):647-57.
Intentional Intravenous Mercury injection. Yudelowitz G. S Afr Med J. 2017 Jan 30;107(2):112-114.
The role of radiology in diagnosis and management of drug mules: an update with new challenges and new diagnostic tools. Schulz B. Grossbach A, et al. Clin Radiol. 2014 Dec;69(12)
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Botulinum, Dimethylmercury, VX, Tetrodotoxin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 8/17/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 8/31/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
VX ("venomous agent X")
LD50 expresses the dose at which 50% of exposed population will die as a result of exposure.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Vaginal pearls, intravaginal foreign bodies (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/20/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 7/21/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Vaginal douching is a common and potentially dangerous practice. Women engage in this practice predominately for personal hygiene reasons but also with the false belief it will prevent or treat infections and for contraception. Numerous public health agencies and medical societies discourage douching as it has been associated with many adverse outcomes including pelvic inflammatory disease, bacterial vaginosis, cervical cancer, low birth weight, preterm birth, human immunodeficiency virus transmission, sexually transmitted diseases, ectopic pregnancy, recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, and infertility.
An increasing fad is the use of intravaginal detox products. Claiming to enhance female health by removing toxins, these mesh cloth-covered balls containing herbs such as mothersworth, osthol, angelica, borneol, and rhizoma, not FDA-approved, are inserted into the vagina for 3 days. Clinical experience demonstrates these products decompose into numerous pieces which become scattered retained intravaginal foreign bodies, cause mucosal irritation, and thereotically could serve as a nidus for serious infections.

Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Antidepressants (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/7/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Lactrodectus (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/29/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 6/30/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Black widow spiders belong to the genus Latro dectus which include 31 species of widow spiders found throughout world. Approximately 1500-2500 black widow bites are reported to American poison control centers annually. A black widow can be identified by their hourglass pattern (red or orange) on the ventral aspect of their shiny globular abdomen. Fortunately, envenomation is rare but when it does occur it causes severe pain, muscle cramping, abdominal (may mimic acute abdomen) often refractory to traditional analgesics and antivenom (Antivenin Latrodectus mactans) is available and effective . Alpha-latrotoxin is the potent toxin causing presynaptic cation channels to open (calcium) and release of neurotransmitters such acetycholine. The neurological signs and symptoms caused by predominantly autonomic and include tachycardia and hypertension. The antivenom is equine based and infused over 20-30 minutes with pain relief in 20 minutes.
Neurotoxic manifestations of black widow spider envenomation in pediatric patients. Sotelo-Cruz N, Gómez-Rivera N. Neurologia. 2016 May;31(4):215-22.
The Black Widow spider bite: differential, clinical manifestations, and treatment options. Shackleford R, Veillon D, Maxwell N, LaChance L, Jusino T, Cotelingam J, Carrington P. J La State Med Soc. 2015 Mar-Apr;167(2):74-8.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Dextromethorphan, Robotripping (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/20/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD

Dextromethorphan Abuse in Adolescence. Bryner JK, Wang K, et al. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 2006;160(12):1217-1222. doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.12.1217.
Dextromethorphan abuse. Antoniou T, Juurlink DN. CMAJ?: Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2014;186(16):E631. doi:10.1503/cmaj.131676.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Pediatric poisoning, household , fatalities (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/30/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Children less than 5 years of age account for the majority of poisoning exposures in the United States. As expected, accessible household items are the most frequently reported exposures and include cosmetics and personal care products, household cleaning substances, medications, and foreign bodies. Opioids are responsible for the highest incidence of hospitalizations followed by benzodiazepines, sulfonylureas, and cardiovascular drugs (beta & calcium channel blockers, and centrally acting antiadrenergic agents). Rise in buprenorphine use has led to significant increases in pediatric exposures. The most common sources of prescription medications were pills found on the ground, in a purse or bag, night stand, or pillbox. The 2015 American Association of Poison Centers Annual report lists 28 fatalities in children less than 5 year of age. Fatalities occurred from exposures to the following: narcotics (9), disc and button batteries (5), carbon monoxide (4), and other substances (10).
Highlighted AAPC cases include:
Poison prevention education of patients prescribed opioids or other highly toxic "one pill killers" who have young children in their household is recommended and could be potentially life saving.
2015 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Centers' National Poison Data System: 33rd Annual Report. Mowrey JB, et al. Clinical Toxicology, 54:10.924-1109.
Emergency Hospitalizations for Unsupervised Prescription Medication Ingestions by Young Children, Lovegrove MC, et al. Pediatrics. 2014,134 (4) e1009-e1016 .
The Underrecognized Toll of Prescription Opioid Abuse on Young Children. Bailey JE, et al. Ann of Emerg Med. April 2009:53(4): 419-24. doi:10.1016/j.annemergmed.2008.07.015.Epub 2008 Sep 6.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Dilantin, Ataxia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/16/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Phenytoin is a first line anticonvulsant agent for most seizure disorders with the exception of absence and toxin-induced seizures. It has erratic gastrointestinal absorption with peak serum levels occurring anywhere from 3-12 hours following a single oral dose. 90% of circulating phenytoin is bound to albumin but only the unbound free fraction is active to cross cell membranes and exert pharmacological effect. Measured serum phenytoin levels reflect the total serum concentration of both the free and protein bound portions. Therapeutic range is between 10-20 mg/L. Free phenytoin levels are not often measured but are normally between 1-2 mg/L. Individuals with decreased protein binding (elderly, malnourished, hypoalbuminemia, uremia, and competing drugs) may have clincial toxicity despite a normal total phenytoin level. Toxicity consists of predominantly ocular and neurologic manifestations involving the vestibular and cerebellar systems:
| Plasma level, µg/mL | Clinical manifestations |
| <10 | Usually none |
| 10-20 | Occasional mild nystagmus |
| 20-30 | Nystagmus |
| 30-40 | Ataxia, slurred speech, extrapyramindal effects |
| 40-50 | Lethargy, confusion |
| >50 | Coma, rare seizures |
Treatment of overdose is primarily supportive with serial drug level testing and neurologic exams. There is no evidence that gastrointestinal decontamination improves outcome. Routine cardiac monitoring is not necessary for overdose following oral ingestions. Cardiac toxicity is rarely seen and only with parenteral administration.
Phenytoin posisoning. Craig S. Neurocrit Care. 2005;3(2): 161-70.
Severe oral phenytoin overdose does not cause cardiovascular morbidity. Wyte CD, et al. Annals of EM. 1997; 20(5). 508-512.
Cardiac Monitoring after phenytoin overdose. Evers M, et al. Heart & Lung. 1997; 26:325-328.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: EDS, Excited Delirium (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/2/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Excited delirium syndrome (EDS) is a life-threatening condition caused by a variety of factors including drug intoxication. EDS is defined as altered mental status, hyperadrenergic state, and combativeness or aggressiveness. It is characterized by tolerance to significant pain, tachypnea, diaphoresis, severe agitation, hyperthermia, non-compliance or poor awareness to direction from police or medical personnel, lack of fatigue, superhuman strength, and inappropriate clothing for the current environment. These patients are at high risk for sudden death. Toxins associated with this syndrome include:
Ketamine at 4mg/kg dose can be given by intramuscular route and has been demonstrated to be safe and effective treatment for EDS.
Top 10 Facts You Need to Know About Synthetic Cannabinoids: Not So Nice Spice Kemp, Ann M. et al. The American Journal of Medicine , Volume 129 , Issue 3 , 240 - 244.
Synthetic cannabinoid drug use as a cause or contributory cause of death. Labay, LM. et al. Forensic Science International , Volume 260 , 31 - 39.
Sudden Death Due To Acute Cocaine Toxicity—Excited Delirium in a Body Packer. Sheilds, LB, Rolf CM, et al. J Forensic Sci, 2015. 60: 1647–1651.
Excited Delirium and Sudden Death: A Syndromal Disorder at the Extreme End of the Neuropsychiatric Continuum. Mash, DC.Frontiers in Physiology. 2016; 7:435.
Prehospital Ketamine is a Safe and Effective Treatment for Excited Delirium in a Community Hospital Based EMS System, Scaggs, TR, Glass, DM, et al. Prehospital and Disaster Medicine. 2016 31(5), 563–569.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Buprenorphine, Suboxone (PubMed Search)
Posted: 2/16/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
The current opioid epidemic is considered the worst drug crisis in American history responsible for 50,000 deaths per year in the US from overdose of heroin and opioid prescription drugs. A 200% increase in the rate of overdose deaths involving opioids occurred between 2000 and 2014. The continued rise in opioid related deaths calls for an urgent need for treatment. Three types of medication-assisted therapies (MATs) are available for treating patients with opioid addiction:methadone, buprenorphine, and naltrexone. Suboxone a combination of buprenorphine and naloxone, is emerging as one of the best choices for the following reasons:
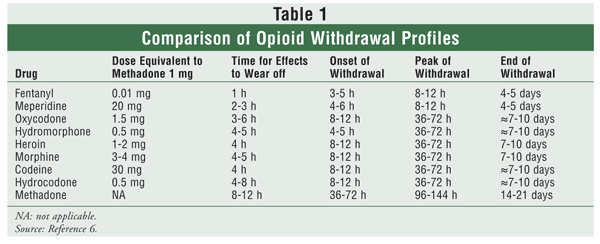
Rudd RA, Seth P, David F, Scholl L. Increase in Drug and Opioid-involved Overose Deaths -Unted States, 2010-2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. ePub: 16 December 2016.
Jones HE. Practical Considerations for the Clinical Use of Buprenorphine. Science & Practice Perspectives. 2004;2(2):4-20.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Urine Drug Sreen (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/19/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 1/20/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Urine drug screens are most commonly performed by immunoassay technology utilizing monoclonal antibodies that recognizes a structural feature of a drug or its metabolites. They are simple to perform. provide rapid screening, and qualitative results on up to 10 distinct drug classes with good sensitivity but imperfect specificity. This can lead to false positive results and the need for confirmatory testing. UDS does not detect synthetic opiates or cannabinoids, bath salts (synthetic cathinones), and gamma-hydroybutyrate. Most common drug classes detected are the following:
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Lactic acidosis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/5/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 1/6/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Lactic acidosis is the most common cause of anion gap metabolic acidosis in all hospitalized patients. An elevated lactate level is an important marker of inadequate tissue perfusion causing subsequent shift to anaerobic metabolism and occuring in a variety of disease states such as sepsis. In patients with unexplained lactic acidosis without systemic hyoperfusion or seizure suspect the following toxins:
Understanding lactic acidosis in paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning. Shah, AD, Wood DM, et al. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2011.71: 20–28.
Value of lactic acidosis in the assessment of the severity of acute cyanide poisoning. Baud FJ, et al. Crit Care Med. 2002;30(9):2044-50.
The Importance of the osmolality gap in ethylene glycol intoxication. Oostvogels R, et al. BMJ 2013 Dec 7;347:31-33.
Can Acute overdose metformin lead to lactic acidosis? Wilis BK, et al. Amer J Emerg Med. 2010;28:857.
Bench to bedside review: Severe lactic acidosis in HIV patients treated with nucleoside analogue reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Classens Y-E, et al. Critical Care. 2003;7(3):226-232.
A case of Kombucha Teas Toxicity. Kole A SH, Jones HD, et al. J Intensive care Med.2009:24(3) 205-7.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Acetaminophen, Liver Failure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/16/2016 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Acetaminophen is one of the most common pharmaceutical ingestions in overdose and a leading cause of acute of liver failure in the U.S. Early recognition and treatment is critical for prevention of morbidity.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Drug Allergy, ADR, ADE (PubMed Search)
Posted: 12/1/2016 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 12/2/2016)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Misclassification of adverse drug effects as allergy is commonly encountered in clinical practice and can lead to use of suboptimal alternate medications which are often less effective.
| DRUGS FREQUENTLY IMPLICATED IN ALLERGIC DRUG REACTIONS | ||
| Aspirin (other analgesics-antipyretics) | Sedative-hypnotics | Iodinated contrast media |
Understanding adverse drug reactions and drug allergies: principles, diagnosis and treatment aspects. Pourpak Z, et al. Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 2008 Jan;2(1):24-46.
Drug Allergy: An Updated Practice Parameter. Joint Task Force. Annals of Allergy, Asthma, & Immunology. Vol 105 ctober , 2010.
Antibiotic allergies in the medical record: effect on drug selection and assessment of validity. Lutomski,DM. Pharmacotherapy. 2008 Nov;28(11) 1348-53.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Poison Ivy, Toxicodendron, Urushiol (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/6/2016 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 10/7/2016)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Fall clean up = Poison Ivy, oak, sumac (Toxicodendron species) which is ubiquitous in North America but it can also be found in British Columbia, Mexico and in parts of Asia. These plants are truly the scourge of outdoor enthusiasts and agricultural workers responsible for up to 40 million cases of miserable often temporarily incapacitating rashes annually.
Fast Facts:
Treatment Tips:
Toxicodendron dermatitis:poison ivy,oak, sumac. Gladman AC. Wilderness Environ Med. 2006. Summer ;17(2):120-8.
Compositions and methods for removing urushiol and treating resulting skin condition.
US 7858570 B2
