Category: Infectious Disease
Keywords: JHR, syphillis, penicillin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/31/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
The Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction (JHR) is a non-specific set of symptoms (fever, malaise, worsened rash, hemodynamic instability, leukocytosis) seen after treating syphillis and other spirochete induced infections. In this study 1 in 4 patients treated with 2.4 million units of benzathine penicillin G developed a short lived JHR. Those who developed the reaction were more likely HIV negative, had secondary syphillis and had successful treatment at 6 months.
Dionne JA, Zhu C, Mejia-Galvis J, et al. Jarisch-Herxheimer Reaction After Benzathine Penicillin G Treatment in Adults With Early Syphilis: Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2025;8(2):e2459490. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.59490
Category: Trauma
Keywords: ASA score, trauma, head injury, prognostication (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/29/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
The American Society of Anesthesia score was an independent predictor of 90-day mortality as
well as low functional status at one year in 720 patients presenting to a single center with
moderate to severe brain injury. When used in conjunction with other prognosticating tools such
as the Trauma and Injury Severity Score, it increased the prognostic value of these scales.
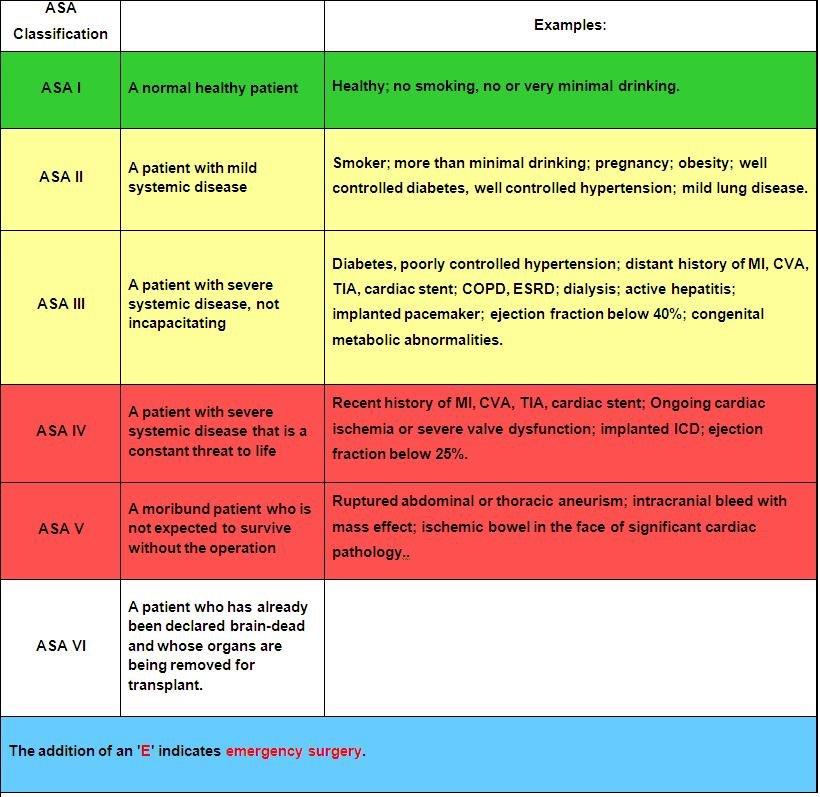
1. Kiwanuka, O., Lassarén, P., Fletcher-Sandersjöö, A. et al. ASA score is an independent
predictor of 1-year outcome after moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury. Scand J Trauma
Resusc Emerg Med 33, 25 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-025-01338-x
2.Statement on ?ASA Physical Status Classification System.
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Trauma, rib fracture, multimodal (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/23/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Controlling pain from rib fractures impacts morbidity and mortality. Over the past decade there has been a focus on decreasing opiate use and approaching this painful condition in a multimodal way. “The multimodal approach utilizes a combination of delivery methods including oral, parenteral, and regional single-shot or catheter-based techniques. Oral medications include opioids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, skeletal muscle relaxants, alpha-2 agonists, mood stabilizers, and neuropathic pain medications. Parenteral medications encompass most of the oral options in addition to ketamine and lidocaine. Regional anesthesia includes epidural analgesia (EA), paravertebral blocks, intercostal blocks, and myofascial plane blocks.”
This study is a single center in Canada looking at medication used for patients admitted over 10 years with rib fractures along with demographics, injury severity and outcomes. The authors concluded:
“Although multimodal pain management strategies have improved over time, a large proportion of patients, even among those with flail chest, still do not receive multimodal pain management. Elderly patients, at highest risk of adverse outcomes, were less likely to receive multimodal pain management strategies and should be the target of performance improvement initiatives.”
Naveed A, Adams-McGavin RC, Ladha K, et al. A 10-year review of pain management practices for rib fractures at a lead trauma hospital: Are we adopting all multimodal pain management strategies? Trauma. 2025;27(1):18-23. doi:10.1177/14604086231198764
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Whole blood, trauma (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/22/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Achieving faster homeostasis in trauma patients leads to lower mortality, less coagulopathy, and lower total blood volume transfusion requirements. This study looked at time to achieving homeostasis as defined by transfusion requirements as well as laboratory measurements in critically ill trauma patients who either received whole blood or component therapy transfusion as part of their resuscitation. Those receiving whole blood achieved statistically significant faster homeostasis.
Chipman, Amanda M. MD; Luther, James F. MA; Guyette, Francis X. MD, MPH; Cotton, Bryan A. MD; Cannon, Jeremy W. MD; Schreiber, Martin A. MD; Moore, Ernest E. MD; Namias, Nicholas MD, MBA; Minei, Joseph P. MD; Yazer, Mark H. MD; Vincent, Laura MS, RN; Cotton, Abigail L. BS, MPH; Agarwal, Vikas MD; Brown, Joshua B. MD, MSc; Leeper, Christine M. MD; Neal, Matthew D. MD; Forsythe, Raquel M. MD; Wisniewski, Stephen R. PhD; Sperry, Jason L. MD, MPH; the SWAT Study Group. Early achievement of hemostasis defined by transfusion velocity: A possible mechanism for whole blood survival benefit. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 98(3):p 393-401, March 2025. | DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004507
Category: Trauma
Keywords: kidney trauma, grading, (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/16/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Unless a patient is unstable, renal injuries are managed non-operatively or endovascularly. Here is the
2025 Kidney Injury Grading Scale from AAST.
AAST AIS
Grade Severity Imaging Criteria
I 2 –Subcapsular hematoma <3.5 cm without active bleeding
– Parenchymal contusion without laceration
II 2 – Parenchymal laceration length <2.5 cm
– HRD <3.5 cm without active bleeding
III 3 – Parenchymal laceration length ?2.5 cm
– HRD ?3.5 cm without active bleeding
– Partial kidney infarction
– Vascular injuries without active bleeding
– Laceration extending into urinary collecting system and/or urinary extravasation
IV 4 – Active bleeding from kidney
– Pararenal extension of hematoma
– Complete/near-complete kidney infarction without active bleeding
– MFK without active bleeding
– Complete/near-complete ureteropelvic junction disruption
V 5 – Main renal artery or vein laceration or transection with active bleeding
– Complete/near-complete kidney infarction with active bleeding
– MFK with active bleeding
Keihani, Sorena MD, MSCI; Tominaga, Gail T. MD; Matta, Rano MD; Gross, Joel A. MD; Cribari, Chris
MD; Kaups, Krista L. MD, MSc; Crandall, Marie MD, MPH, FACS; Kozar, Rosemary A. MD; Werner,
Nicole L. MD, MS; Zarzaur, Ben L. MD; Coburn, Michael MD, FACS; Myers, Jeremy B. MD, FACS. Kidney
organ injury scaling: 2025 update. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 98(3):p 448-451, March
2025. | DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004509
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Sarcopenia, trauma, ct scan (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/9/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Having a readily measurable variable to identify frailty on admission for critically injured patients would help prognosticate morbidity, mortality, and discharge destination. Sarcopenia has been used to prognosticate length of stay, discharge destination, and physical function recovery in oncology and general surgery patients. Sarcopenia is defined as “age-related progressive loss of muscle mass and strength. The main symptom of the condition is muscle weakness. Sarcopenia is a type of muscle atrophy primarily caused by the natural aging process. Scientists believe being physically inactive and eating an unhealthy diet can contribute to the disease.” 1. This study looked at admission CT scan psoas muscle sarcopenia in 197 critically injured patients. The authors concluded:
“For trauma critical care patients, sarcopenia on admission CT was associated with dependent discharge destination and therefore is unfavourable. Defining sarcopenia early in a trauma patient’s critical care admission may help to identify those at risk of poor outcomes.” 2
1. Sarcopenia (Muscle Loss): Symptoms & Causes
2. Badminton R, Christie R, Brohi K, Cole E. Pre-injury sarcopenia and the association with discharge destination in critical care trauma patients. Trauma. 2025;27(1):57-64. doi:10.1177/14604086231214878
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Male. Female, outcome, trauma (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/6/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
The Pan-Asia Trauma Outcomes Study database was reviewed for differences in in-hospital mortality and functional capacity at discharge between male and female trauma patients. There were 76,000 trauma patients from 12 Asian countries in this study. The authors concluded: “This study indicates no difference in the general trauma outcomes in the Asia Pacific between females and males. Although younger females with less severe injuries had better functional outcomes, this advantage disappeared in severe injuries and those over 50 years.” There were several differences in mechanism of injury and age of presentation. “With females more frequently represented in the ??50 age group (60.13%) compared to males (44.87%) (p?<?0.001). Trauma type also varied between sexes; 95.51% of females experienced blunt trauma compared to 93.65% of males (p?<?0.001). Anatomically, males predominantly sustained injuries to the head, face, thorax, abdomen, and upper extremities, whereas females more frequently suffered injuries to the lower extremities and spine (p?<?0.001).” This is similar toEuropean and North American data
Bin Kunji Mohamad, M., Jamaluddin, S.F., Ahmad, N. et al. Trauma outcomes differences in females: a prospective analysis of 76 000 trauma patients in the Asia-Pacific region and the contributing factors. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 33, 34 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-025-01342-1
Category: Trauma
Keywords: EMS, AlS, trauma, Bls, outcome (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/5/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Large retrospective propensity matching study looking at mortality in trauma patients based on ALS vs. BLS transport crew found lower mortality in those attended by ALS crews. The matching was “based on patient age, sex, year, ICD-10-CM based injury severity score, mechanism of injury, AIS based body region of injury, EMS characteristics including time with patient and prehospital interventions performed, prehospital vital signs, and trauma center designation.”
This is different than other studies which showed limited difference. other studies have shown improved survival with police “scooping and running” with penetrating trauma patients.

Harrison, Julia MD; Bhardwaj, Akshay MS; Houck, Olivia MPH; Sather, Kristiana MD; Sekiya, Ayako MPH; Knack, Sarah MD; Saarunya Clarke, Geetha PhD; Puskarich, Michael A. MD, MSCR; Tignanelli, Chris MD, MSc; Rogers, Lisa MPH; Marmor, Schelomo PhD; Beilman, Greg MD. Emergency medical services level of training is associated with mortality in trauma patients: A combined prehospital and in hospital database analysis. Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 98(3):p 402-409, March 2025. | DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004540
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Trauma, geriatric, fall, pain management, fracture, rib, pelvis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/1/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 3/2/2025)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Rib and pelvic fractures are common findings in geriatric trauma patients, even in low impact trauma such as falls from standing. Pain management is vital for improving morbidity and mortality. The IFEM White Paper suggests:
“Use multimodal pain management strategies, including regional anesthesia and non-opioid analgesics, to control pain without compromising recovery.
Monitor closely for complications such as pneumonia or hemodynamic instability, intervening promptly to mitigate risks.
Collaborate with physiotherapists to implement early mobility programs, reducing the risk of deconditioning and promoting recovery.”
A multidisciplinary team proficient in geriatric trauma care leads to better outcomes. This may require transfer to a trauma center.
Trauma in Older Adults: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Optimized Care White Paper
Trauma Special Interest Group and Geriatric Emergency Medicine Special Interest Group
https://assets.nationbuilder.com/ifem/pages/1768/attachments/original/1740084007/IFEM_Trauma_in_Older_Adults_Evidence-Based_Guidelines_for_Optimized_Care_White_Paper_December_2024.pdf?1740084007
Published: December 2024
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Trauma, geriatrics, frailty (PubMed Search)
Posted: 3/1/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
This white paper reminds us that age is just a number; frailty is a better predictor of morbidity and mortality after trauma.
“Frailty, characterized by reduced physiological reserve and increased vulnerability to stressors, is a significant factor influencing recovery from trauma. Individuals with frailty may experience slower healing, higher rates of complications, and longer hospital stays. Tools such as the Clinical Frailty Scale (CFS) and the Trauma-Specific Frailty Index (TSFI) have been developed to assess frailty systematically, enabling clinicians to predict outcomes and guide treatment decisions.”
Trauma in Older Adults: Evidence-Based Guidelines for Optimized Care White Paper
Trauma Special Interest Group and Geriatric Emergency Medicine Special Interest Group
https://assets.nationbuilder.com/ifem/pages/1768/attachments/original/1740084007/IFEM_Trauma_in_Older_Adults_Evidence-Based_Guidelines_for_Optimized_Care_White_Paper_December_2024.pdf?1740084007
Published: December 2024
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Ems, trauma, arrest, resuscitation (PubMed Search)
Posted: 2/23/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
This position paper from American College of Surgeons, NAEMSP, and ACEP outlines a literature based approach to prehospital care of traumatic circulatory arrest. It logically could be applied to care in the hospital as well. Care of a traumatic arrest is different than a medical etiology arrest.
“Emphasize the identification of reversible causes of traumatic circulatory arrest and timely use of clinically indicated life-saving interventions (LSIs) within the EMS clinician’s scope of practice. These include:
Epinephrine should not be routinely used, and if used should not be administered before other LSIs.
External chest compressions may be considered but only secondary to other LSIs.
Chest decompression if there is clinical concern for a tension pneumothorax. Empiric bilateral decompression, however, is not indicated in the absence of suspected chest trauma.
Airway management using the least-invasive approach necessary to achieve and maintain airway patency, oxygenation, and adequate ventilation.
External hemorrhage control with direct pressure, wound packing, and tourniquets.”
Amelia M. Breyre, Nicholas George, Alexander R. Nelson, Charles J. Ingram, Thomas Lardaro, Wayne Vanderkolk, John W. Lyng,
Prehospital Management of Adults With Traumatic Out-of-Hospital Circulatory Arrest—A Joint Position Statement,
Annals of Emergency Medicine,
Volume 85, Issue 3,
2025,
Pages e25-e39,
ISSN 0196-0644,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2024.12.015.
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Peds, trauma, centers, adolescents (PubMed Search)
Posted: 2/16/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Looking at 416 patients aged 12-16, 48% at a Peds trauma center vs 20% at adult Level 1 center vs 34% at an adult level 2 center, there was no difference in in hospital mortality between adult and pediatric centers.
The authors conclude “These findings suggest that severely injured adolescents aged 12 to 16 years may be safely treated at either adult or pediatric trauma centers.”
Muttalib F, Tillmann B, Ernst G, Murthy S, Bhutta Z, Hansen B, Adhikari NKJ. Mortality Among Severely Injured Adolescents Admitted to Pediatric vs Adult Trauma Centers. JAMA Netw Open. 2024 Dec 2;7(12):e2450647. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.50647.
Category: Cardiology
Keywords: Hypertension, as needed, acute kidney injury (PubMed Search)
Posted: 2/9/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
A retrospective look at veterans who received oral and/or IV as needed blood pressure medications while hospitalized in a non-ICU setting found an association with as needed meds and acute kidney injury, greater than 25% blood pressure drop in 3 hours, and death, stroke and MI while hospitalized. IV medications had a higher association.
While needing prospective validation, this appears to be more evidence to treat the patient not the number.
Canales MT, Yang S, Westanmo A, Wang X, Hadley D, Ishani A, Mohandas R, Shorr R, Lo-Ciganic W. As-Needed Blood Pressure Medication and Adverse Outcomes in VA Hospitals. JAMA Intern Med. 2025 Jan 1;185(1):52-60. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2024.6213. PMID: 39585709; PMCID: PMC11589853.
Category: Infectious Disease
Keywords: Risk, soft tissue, infection (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/30/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/2/2025)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Risk factors for necrotizing soft tissue infections include: obesity, diabetes mellitus, peripheral vascular disease, immunosuppression, injection drug use, and deep traumatic wounds.
“Any anatomical site can be involved, but the most common sites are perineal, anorectal, foot, or lower extremities.”
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Cervical sound, age, geriatric, trauma, clearance (PubMed Search)
Posted: 2/1/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Not based on currently available literature.
This editorial reminds us that the only evidenced based screening criteria we have for C-spine clearance in those over age 65 after trauma is the Canadian C-Spine Rule (2002). This rule recommends imaging for all patients over age 65. No large, well done study indicates physical exam or other means can be used to clear C-Spines in those over age 65.
Rodriguez R, Greenberg S. Is older age an appropriate criterion alone for ordering cervical spine CT after trauma. Acad Emerg Med. 2024; 00: 1-2. doi:10.1111/acem.15001
Category: Infectious Disease
Keywords: Soft tissue infection (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/30/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
These infections remain difficult to diagnose early and early diagnosis is key to limiting morbidity and mortality.
“The classic clinical signs and symptoms are rarely all present especially in early disease. Crepitus or gas in the soft tissues, while specific, is only present in approximately 10% of patients. More often, the presenting symptoms are nonspecific: fever, pain, induration, and edema. Pain out of proportion to examination is a more specific finding that may assist in differentiation of NSTI from cellulitis.”
Bisgaard, Erika K. MD; Bulger, Eileen M. MD
Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery 97(5):p 678-686, November 2024. | DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000004351
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Chest trauma, ketorolac, ketamine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/26/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
This small study randomized patients with 2 or greater rib fractures or requiring chest tube insertion into a kerorolac (30 mg) or ketamine (0.25 mg/kg) group and evaluated pain levels pre, 30 and 60 minutes post medication administration. They also looked at need for morphine rescue medication. The ketamine group had superior pain control and required less rescue medication.
Hossein Zabihi Mahmoodabadi MD, Zeynab Seyed Javadein MD, Fatemeh Moosaie MD, MPH, Ali Faegh, Maryam Bahreini MD
First published: 31 December 2024
Category: Trauma
Keywords: occipital, condyles, fracture, cervical spine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/19/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
Fractures of the occipital condyles are a relatively rare injury that occur in high energy blunt mechanisms (IE roll over MVC) most commonly. Physical exam will show signs of basilar skull fracture and significant pain at the base of the skull/upper C-spine. CT scan is the gold standard to make the diagnosis. Look for signs of upper extremity weakness on physical exam or cranial nerve injuries. Those type of findings should also prompt emergent MRI evaluation. Treatment generally is long term immobilization in a collar however Type 3 and those with neurologic findings may require surgical intervention.
Anderson and Montesano Classification
Type I 3% of occipital condyle fracturesImpaction-type fracture with comminution of the occipital condyle
Due to compression between the atlantooccipital joint
Stable injury due to minimal fragment displacement into the foramen magnum
Type II 22% of occipital condyle fracturesBasilar skull fracture that extends into one or both occipital condyles
Due to a direct blow to skull and a sheer force to the atlantooccipital joint
Stable injury as the alar ligament and tectorial membrane are usually preserved
Type III 75% of occipital condyle fractures Avulsion fracture of condyle in region of the alar ligament attachment (suspect underlying occipitocervical dissociation)
Due to forced rotation with combined lateral bending
Has the potential to be unstable due to craniocervical disruption

Category: Pharmacology & Therapeutics
Keywords: tpa, frostbite, iloprost, therapy (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/13/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
This meta analysis of studies looking at thrombolytics and prostaglandins in treating significant frost bite offers some insight into the possibilities these therapeutics offer. Unfortunately, the studies available are not high quality and most are case reports.
“Our results suggest that thrombolysis or intravenous iloprost is effective when administered promptly to treat severe frostbite. For grade 3–4 frostbite the Wilderness Medical Society frostbite guidelines recommend the use of intravenous iloprost within 48 h of injury, and thrombolysis within 24 h of injury. The Helsinki protocol recommends the use of tPA for patients with grade 3–4 frostbite presenting within 48 h of injury with angiographic evidence of thrombosis."
“Iloprost is a synthetic prostaglandin I2 that has been used to treat frostbite . Like other prostacyclins, it inhibits platelet aggregation and promotes vasodilation. Iloprost may stimulate the release of endogenous tissue plasminogen activator or counteract its inhibitory effects [35]. Iloprost reduces vasoconstriction induced by thromboxane A2 , and may reduce oxidative stress from free radicals, moderating reperfusion injury [37, 38]. The effect on platelet aggregation may be reversed within two hours), but prostacyclin effects may disrupt the vicious cycle of activated platelets and leukocytes that damages endothelium .”
More research in this area is needed. Transfer to a center with these capabilities seems worth a discussion in the case of severe frostbite.
Regli, I.B., Oberhammer, R., Zafren, K. et al. Frostbite treatment: a systematic review with meta-analyses. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 31, 96 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-023-01160-3
Category: Trauma
Keywords: Frail, trauma, mortality, outcome (PubMed Search)
Posted: 1/12/2025 by Robert Flint, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Robert Flint, MD
The Trauma Frailty Index has been validated to predict inpatient mortality, major complications and discharge to rehab facility. “In addition, frailty was significantly associated with higher adjusted odds of mortality, major complications, readmissions, and fall recurrence at 3 months postdischarge ( p < 0.05).”
It is a simple 15 variable index.

Joseph B, Saljuqi AT, Amos JD, Teichman A, Whitmill ML, Anand T, Hosseinpour H, Burruss SK, Dunn JA, Najafi K, Godat LN, Enniss TM, Shoultz TH, Egodage T, Bongiovanni T, Hazelton JP, Colling KP, Costantini TW, Stein DM, Schroeppel TJ, Nahmias J; AAST Frailty MIT Study Group. Prospective validation and application of the Trauma-Specific Frailty Index: Results of an American Association for the Surgery of Trauma multi-institutional observational trial. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2023 Jan 1;94(1):36-44. doi: 10.1097/TA.0000000000003817. Epub 2022 Oct 17. PMID: 36279368.
