Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Hemodialysis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 11/2/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
The cornerstone treatment of poisoning is removal of the toxin from the patient. This can be accomplished before absorption into the body by decontamination methods (dermal or gastrointestinal) or after absorption by blocking metabolism of parent compound, displacing drugs from receptors, binding toxins with neutralizing agents (chelators, Fab fragments), or enhancing elimination by dialysis. Toxins that are ideal candidates for dialysis include substances that are low molecular weight, have low volume of distribution (stay in the blood stream), or low protein binding. Toxins most commonly treated with dialysis are:
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: strychnine (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/26/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 10/27/2017)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Her first book “The mysterious affair at Styles,” Agatha Christie introduced her lead detective in her novels, Hercule Poirot - the Belgian detective. She also described the death of Mrs. Emily Inglethorp by strychnine.
Strychnine is found in a disc-like seed of strychnos nux-vomica, a tree native to tropical Asia and North Australia.
It is currently used as rodenticide (moles and gophers), in Chinese herbal medicine and a traditional remedy in Cambodia.
Strychnine inhibits binding of glycine (a major inhibitory neurotransmitter in spinal cord) to Cl-channel resulting in identical clinical syndrome – seizure-like generalized muscle contraction with normal mental status – as tetanus toxin. Tetanus toxin inhibits the release of presynaptic glycine in the spinal cord.
Management
Goal: decrease muscle hyperactivity
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Arsenic poisoning (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/19/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Agatha Christie is an English crime novelist who frequently used poisons in her books to murder the victims. In her book, Murder is Easy, Ms. Christie uses arsenic/arsenic trioxide to kill several characters.
Primary source of arsenic in general population is contaminated food, water and soil. Arsenic exists in several forms: elemental, gaseous (arsine), organic and inorganic (trivalent or pentavalent).
Arsenic trioxide has also been used to treat acute promyelocytic leukemia in China; it’s use in other leukemia, lymphoma, and other solid tumors are currently being investigated.
Arsenic primarily inhibits the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex and multiple other enzymes involved in the citric cycle/oxidative phosphorylation, resulting in mitochondrial dysfunction.
Acute toxicity of arsenic after ingestion
Management
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Cannabinoid, cyclic vomiting, Capsaicin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/12/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Cannabinoid hyperemesis is a syndrome (CHS) characterized by severe intractable nausea, cyclical vomiting, and abdominal pain associated with chronic marijuana abuse. It is often a underrecognized cause of cyclic vomiting syndrome. Despite well established anti-emetic properties of marijuana, paradoxical effects on the GI tract exist through cannabinoid receptors which exert their neuromodulatory properties in the central nervous system and the enteric plexus. Multiple theories of mechanism of CHS are in the literature. Diagnosis is based on the following clinical criteria:
Acute care goals are to treat dehydration and terminate nausea and vomiting. Administration of intravenous fluids, dopamine antagonists, topical capsaicin cream, and avoidance of narcotic medications are recommened treatment measures. Benzodiazepines followed by haloperidol and topical capsaicin are reported to be most effective. Capsaicin activates the transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 receptors (TRPV1) which impairs substance P signalling in the area postrema and nucleus tract solitarius similar to noxious stimuli, such as heat.
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome: Diagnosis, Pathophysiology, and Treatment-a Systematic Review. Sorensen CJ, DeSanto K, et al. J Med Toxicol. 2017 Mar;13(1):71-87.
Cannabinoid Hyperemesis and Compulsive Bathing: A Case Series and Paradoxical Pathophysiological Explanation. Patterson D, Smith E, et al. Am Board Fam Med. 2010 Nov-Dec; 23(6): 790-793.
Pharmacologic treatment of cannabinoid hyperemesis Syndrome: A systematic review. Pharmacotherapy. Dezieck L, Hafez Z. 2017 Jun:37(6):725-734.
Resolution of cannabis hyperemesis syndrome with topical capsaicin in the emergency department: a case series. Dezieck L, Hafez Z, et al. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2017 Sep;55(8):908-913.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Capsaicin, hunan hand, chili peppers (PubMed Search)
Posted: 10/6/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Hunan hand syndrome is a painful contact dermatitis that frequently presents in cooks and chili pepper workers after preparing or handling chili peppers. Contact with other body parts gives rise to the terms: "Hunan nose" ''Hunan eye",and "Chili Willie". Capsaicin, found in the fruit of plants from the genus Capsicum such as red chili peppers, jalapeños, and habaneros, is a hydrophobic, colorless, odorless compound that binds with pain receptors causing the sensation of intense heat or burning. The "heat" or pungency of a peppers is measured in Scoville heat units (SHU), the number of times a chili extract must be diluted with water to lose heat. Habanero peppers generate 30,000 SHU. Even at low concentrations capsaicin is a skin irritant. It is the primary ingredient in pepper spray used in law enforcement and in personal defense sprays.
Treatment consists of decontamination with water irrigation for opthalmic exposure and milk or antacids for dermal or gastrointestinal exposure. Burning can be recurrent and of of long duration depending on tissue penetration. Topical anesthetic especially for the eye and cool compresses for the skin can relieve pain. Parodoxically capsaicin is used as a topical analgesic medication for local pain relief from muscle pain, itching, and painful neuropathies (diabetic, postherpetic). Capsaicin initially causes neuronal excitation followed by a long-lasting refractory period due to depletion of substance P, during which neurons are no longer responsive to a large range of stimuli and thus are desensitized.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Hyperkalemia (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/22/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 10/5/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Hyperkalemia is a potentially life threatening problem which can lead to cardiac dysrhythmias and death. Drug interactions inducing hyperkalemia are extremely common such as the combination of ACE inhibitors and spironolactone or ACE inhibitors and trimehoprim sulfamethoxazole. Hyperkalemia can also occur with a single agent and is a relatively common complication of therapy with trimethoprim sulfamethoxazole. The following drugs can cause hyperkalemia:
Drug induced hyperkalemia. Salem B. Badreddine A, et al. Drug Safety 2014 Sept;37(9) 677-92.
Beta-blockers, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, and the risk of hyperkalemia requiring hospitalization in the elderly: a nested case-control study. Weir MA, Juurlink DN, et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;5:1544-1551.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: SGLT2 inhibitors, diabetes (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/14/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
During the past several years, several new classes of diabetic medications were introduced for clinical use, including SGLT2 inhibitors (canagliflozin, dapagliflozin and empagliflozin).
SGLT2 inhibitors prevent reabsorption of glucose in the proximal convoluted tubules in the kidney and does not alter insulin release.
A recent retrospective study (n=88) of 13 poison center data from January 2013 to December 2016 showed
49 patients were evaluated in a health care facility (HCF) with 18 admissions. Referral to HCF was more common in pediatric patients. This was likely due to unfamiliarity with a new mediation and lack of toxicity data.
Other case reports have shown higher incidence of DKA with the therapeutic use of SGLT2 vs. other classes of DM medications.
Bottom line:
Limit data is available regarding the toxicologic profile of SGLT2 inhibitors.
Based upon this small retrospective study, hypoglycemia may not occur and majority of the patient experience minimal symptoms.
Schaeffer SE et al. Retrospective review of SGLT2 inhibitor exposures reported to 13 poison center. Clin Toxicol (Phila).2017 Aug 16:1-5 PMID: 28812381
Burke KR et al. SGLT2 inhibitors: a systematic review of diabetic ketoacidosis and related risk factors in the primary literature. Pharmacothearpy. 2017;37:187-194
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Radiographs, poisoning (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/7/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 9/8/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Radiographs studies can be valuable in poisoning diagnosis, management, and prognosis. Radiographic imaging should be utilized for the following toxins:
Container toxins - Body packers
Sustained Released preparations
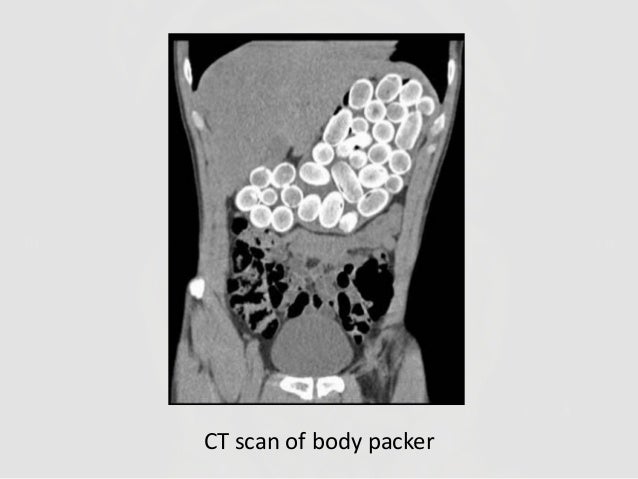
Plain adominal radiography: a powerful tool to prognosticate outcome in patients with zinc phosphide. Hassanian-Moghaddam H, Shahnazi M, et al. Clin Radiolol. 2014. Oct;69 (10);1062-5.
Systemic Plumbism following remote ballistic injury, Reinboldt M, Franics K, Emerg Radio. 2014 Aug:21 (4): 423-6.
Lead arthropathy: radiographic, CT, and MRI findings, Fernandes JL, Rocha AA, et al. Skeletal Radiol. 2007 Jul;36(7):647-57.
Intentional Intravenous Mercury injection. Yudelowitz G. S Afr Med J. 2017 Jan 30;107(2):112-114.
The role of radiology in diagnosis and management of drug mules: an update with new challenges and new diagnostic tools. Schulz B. Grossbach A, et al. Clin Radiol. 2014 Dec;69(12)
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: fentanyl, first responder exposure (PubMed Search)
Posted: 9/7/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
There have been reports of “intoxication” or adverse effects among first responders and law enforcement due to exposure to a “powder” suspected to be fentanyl or its analog.
This has led to a significant concern among first responders and law enforcement when investigating or handling “powder” at the scene of overdose or drug enforcement related raids. (http://www.foxnews.com/health/2017/08/15/police-department-gets-hazmat-like-protective-gear-for-overdose-calls.html)
American College of Medical Toxicology and American Association of Clinical Toxicology recently published a position statement to help clarify the potential health risk associated with exposure to fentanyl and its analogs.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Botulinum, Dimethylmercury, VX, Tetrodotoxin (PubMed Search)
Posted: 8/17/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 8/31/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
VX ("venomous agent X")
LD50 expresses the dose at which 50% of exposed population will die as a result of exposure.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: dabigatran reversal, Idarucizumab (PubMed Search)
Posted: 8/25/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Full cohort analysis idarucizumab for dabigatran associated bleeding was recently published in NEJM.
This study evaluated the laboratory correction of elevated ecarin clotting time or diluted thrombin time induced by dabigatran and time to either cessation of bleeding (Group A: patients with GI bleeding, traumatic bleeding, or ICH) or time to surgery (Group B: patients requiring surgical intervention within 8 hours).
Findings
Group A (n=301): Median time to the cessation of bleeding was 2.5 hours in 134 patients.
HOWEVER:
Group B (n=202): Median time to intended surgery after infusion of idarucizumab was 1.6 hours.
Laboratory markers:
100% reversal of abnormal ecarin clotting time or diluted thrombin time within 4 hours after the administration
Mortality
Conclusion
Authors concluded thate idaurcizumab is an "effective" reversal agent for dabigatran.
Overall, the findings are more promising compared to the interim analysis that was published in 2015.
Other findings:
Infusion of idarucizumab decreased the dabigatran level from 110 ng/mL (Group A) and 73.6 ng/mL (Group B) to < 20 ng/mL.
Rebound levels of > 20 ng/mL were noted in 191 patients after 12 – 24 hours after idarucizumab adminiatration
Thrombotic events occured in 24 patients (14 in Group A and 10 in Group B) within 30 days after treatment
Serious adverse events occured in 23.3% of the patients within 5 days.
Most frequent events were:
Pollack CV et al. Idarucizumab for dabigatran reversal - full cohort analysis. N Eng J Med 2017;377:431-41.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: salicylate poisoning, endotracheal intubation, hemodialysis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/27/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Patients with severe salicylate poisoning may require endotracheal intubation due to fatigue from hyperventilation or mental status change.
A previously published study (Stolbach et al. 2008) showed that mechanical ventilation increases the risk of acidemia and clinical deterioration.
A small retrospective study investigated the impact of hemodialysis (HD) in intubated patients with salicylate poisoning.
Findings:
53 cases with overall survival rate of 73.2%
In patients with salicylate level > 50 mg/dL
If salicylate level > 80 mg/dL
Bottom Line:
There is moratality benefit of HD in intubated salicylate-poisoned patient.
McCabe DJ, Lu JJ. The association of hemodialysis and survival in intuated salicylate-poisoned patients. Amer J Emerg Med 2017;35:899-903.
Stolbach QI, Hoffman RS, Nelson LS. Mechanical ventilation was associated with acidemia in a case series of salicylate-poisoned patients. Acad Emerge Med 2008;15;866-869.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Vaginal pearls, intravaginal foreign bodies (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/20/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 7/21/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Vaginal douching is a common and potentially dangerous practice. Women engage in this practice predominately for personal hygiene reasons but also with the false belief it will prevent or treat infections and for contraception. Numerous public health agencies and medical societies discourage douching as it has been associated with many adverse outcomes including pelvic inflammatory disease, bacterial vaginosis, cervical cancer, low birth weight, preterm birth, human immunodeficiency virus transmission, sexually transmitted diseases, ectopic pregnancy, recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis, and infertility.
An increasing fad is the use of intravaginal detox products. Claiming to enhance female health by removing toxins, these mesh cloth-covered balls containing herbs such as mothersworth, osthol, angelica, borneol, and rhizoma, not FDA-approved, are inserted into the vagina for 3 days. Clinical experience demonstrates these products decompose into numerous pieces which become scattered retained intravaginal foreign bodies, cause mucosal irritation, and thereotically could serve as a nidus for serious infections.

Category: Toxicology
Keywords: hydrogen peroxide (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/13/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a common household liquid that is used for wound irrigation/antiseptic and cosmetic purposes. The concentration of household product is 3% to 5% and is considered to be relatively safe except in large volume ingestion.
High-concentration H2O2 (>10%) is commercially available as “food grade” (35%) that is diluted for household use or for alternative medicine therapy (i.e. hyperoxygenation).
Ingestion of high-concentration of H2O2 can result in caustic injury as well as ischemic injury from gas embolism.
Ingestion of 1 mL of 3% H2O2 produces 10 mL of O2 gas while 1 mL of 35% H2O2 produces 115 mL of O2 gas.
Common symptoms/findings of H2O2 ingestions includes:
A retrospective review of >10% H2O2 ingestion from National Poison Data System showed:
Management
Hatten BW et al. Outcomes after high-concentration peroxide ingestions. Ann Emerg Med. 2017;69:726-736.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Antidepressants (PubMed Search)
Posted: 7/7/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Lactrodectus (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/29/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
(Updated: 6/30/2017)
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD
Black widow spiders belong to the genus Latro dectus which include 31 species of widow spiders found throughout world. Approximately 1500-2500 black widow bites are reported to American poison control centers annually. A black widow can be identified by their hourglass pattern (red or orange) on the ventral aspect of their shiny globular abdomen. Fortunately, envenomation is rare but when it does occur it causes severe pain, muscle cramping, abdominal (may mimic acute abdomen) often refractory to traditional analgesics and antivenom (Antivenin Latrodectus mactans) is available and effective . Alpha-latrotoxin is the potent toxin causing presynaptic cation channels to open (calcium) and release of neurotransmitters such acetycholine. The neurological signs and symptoms caused by predominantly autonomic and include tachycardia and hypertension. The antivenom is equine based and infused over 20-30 minutes with pain relief in 20 minutes.
Neurotoxic manifestations of black widow spider envenomation in pediatric patients. Sotelo-Cruz N, Gómez-Rivera N. Neurologia. 2016 May;31(4):215-22.
The Black Widow spider bite: differential, clinical manifestations, and treatment options. Shackleford R, Veillon D, Maxwell N, LaChance L, Jusino T, Cotelingam J, Carrington P. J La State Med Soc. 2015 Mar-Apr;167(2):74-8.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: drugs of abuse, street name (PubMed Search)
Posted: 6/5/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 6/15/2017)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Street names for illicit substance are diverse and unique. Knowing what your patient used prior to ED presentation can help with the management of their intoxication.
DEA recently released 7 page list of common street names for drugs of abuse.
https://ndews.umd.edu/sites/ndews.umd.edu/files/dea-drug-slang-code-words-may2017.pdf
But keep in mind that what our patients purchase and use may not actually contain the drug that they intended to purchase (e.g. fentanyl being sold as heroin).
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: foodborne botulism (PubMed Search)
Posted: 5/25/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Botulism is a rare neurologic condition characterized by GI symptoms that progressed to cranial nerve dysfunction and symmetric descending paralysis. Foodborne botulism is due to ingestion of botulinum toxin that is produced by clostridium botulinum, an ubiquitous bacterium in our environment.
Bottom line:
Maryland Department of Health and Mental Hygiene
CDC Emergency Operations Center: 770-488-7100
Foodborne botulism is characterized by
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: Dextromethorphan, Robotripping (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/20/2017 by Kathy Prybys, MD
Click here to contact Kathy Prybys, MD

Dextromethorphan Abuse in Adolescence. Bryner JK, Wang K, et al. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 2006;160(12):1217-1222. doi:10.1001/archpedi.160.12.1217.
Dextromethorphan abuse. Antoniou T, Juurlink DN. CMAJ?: Canadian Medical Association Journal. 2014;186(16):E631. doi:10.1503/cmaj.131676.
Category: Toxicology
Keywords: lactic acidosis (PubMed Search)
Posted: 4/20/2017 by Hong Kim, MD
(Updated: 2/1/2026)
Click here to contact Hong Kim, MD
Lactic acids are often elevated in critical care patients (e.g. septic shock). It can be also elevated in setting of drug overdose or less frequently in therapeutic use due to interference of oxidative phosphorylation. Some of the agents include:
Bottom line:
Kraut JA, Madias NE. Lactic acidosis, N Engl J Med 2014;371:2309-19.
